DRPC Overview
DRPC serves as a gateway for Web3 developers and users to access a distributed network of independent third-party partners and public nodes.
DRPC's infrastructure consists of several key components. At the core of the infrastructure is Dshackle (opens in a new tab), an open source library created by the Emerald company, which is used to provide stable routing to multiple nodes and ensure the resilience of the network. It’s worth to mention that we use our own fork of Dshackle (opens in a new tab).
Dproxy acts as a gateway proxy to the network of independent third-party partners and public nodes, distributing workload and ensuring efficient handling of requests.
Data providers
DRPC's data providers are independent third-party companies that own and operate the blockchain infrastructure. These providers are carefully selected based on their reliability, quality of service, and other factors.
DRPC asks each provider to install its own instance of Dshackle, which provides stable routing to multiple nodes and ensures that each request is executed on an appropriate node, taking into account node location, state, current height, RPC methods, and other characteristics.
DRPC request execution
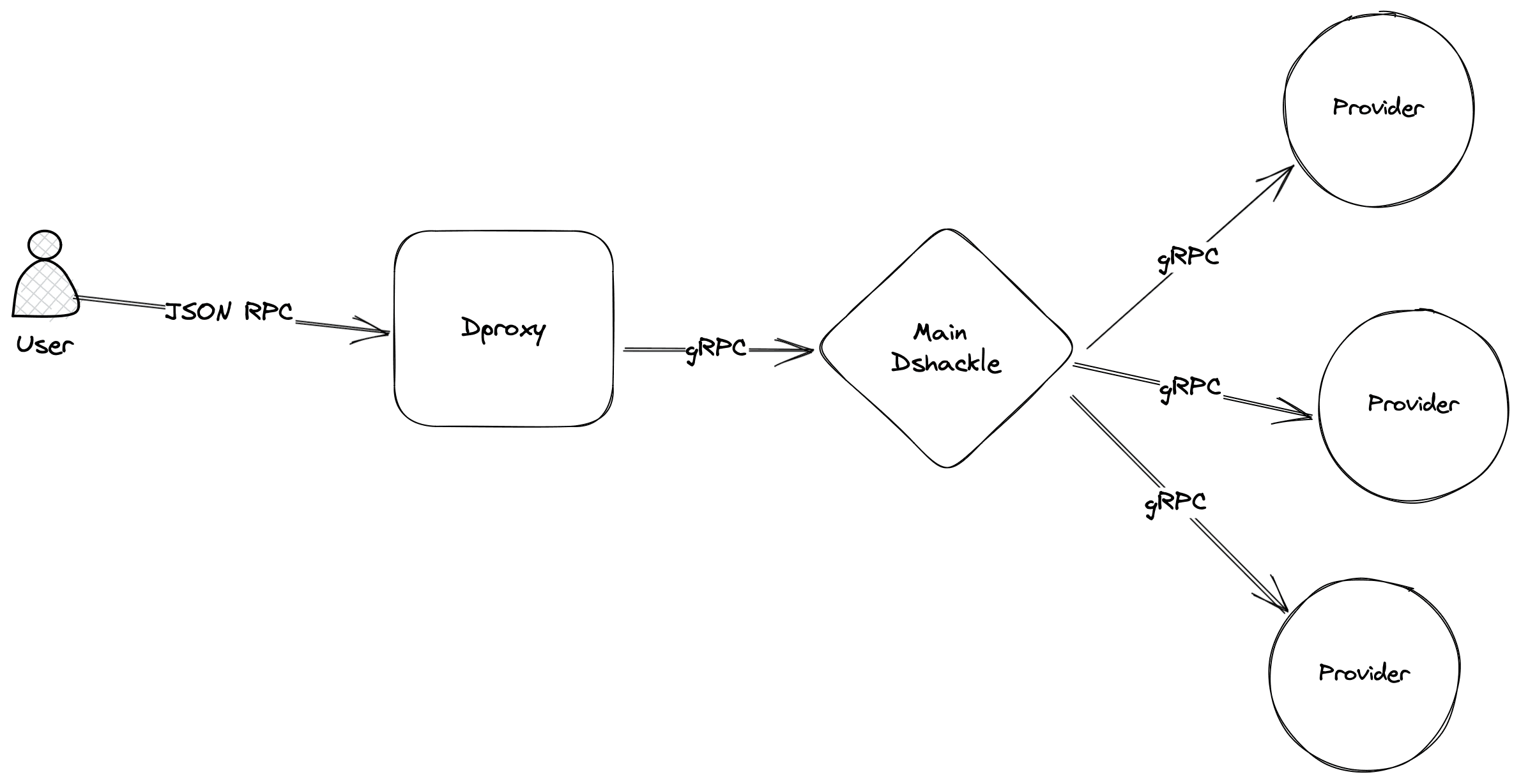
When a user submits a request through DRPC, it is received by the Dproxy. Dproxy then uses its routing algorithms to select an appropriate data provider to handle the request, based on various factors such as location, capacity, recent performance and other characteristics.
Once the data provider is selected, Dproxy sends the request to the main Dshackle instance, which serves as a central hub for routing requests and aggregating data from the various data providers. Main Dshackle then forwards the request to the selected data provider's own instance of Dshackle, which executes the request and returns the result to the main Dshackle.
Why Dshackle?
First, Dshackle is an open-source library that has been used in production environments for a considerable amount of time, giving it a proven track record for reliability and stability.
Second, Dshackle provides a number of useful features for routing and load balancing, such as the ability to track nodes’ current chain heads, as well as the ability to prioritize or deprioritize nodes based on their status and other factors. This allows DRPC to ensure that each request is executed on an appropriate provider, taking into account node location, state, current height, RPC methods, and other characteristics.
- When sending a transaction: Dshackle will broadcast it to all available nodes.
- When retrieving a balance: Dshackle will only consider nodes that have no lag to get the most up-to-date balance information.
- For methods that require data from a specific block: Dshackle will only select nodes that have already synced up to that block. This is to ensure that the data is accurate and the request is fulfilled quickly.
By handling different methods in these ways, Dshackle ensures that requests are routed to the most appropriate nodes, and that the data returned is accurate and up-to-date.
Finally, by using Dshackle as an abstraction between DRPC and the data providers, DRPC is able to provide its partners with a great deal of flexibility in how they configure and manage their infrastructure. This allows each provider to optimize their setup for their specific use case, while still being part of a larger decentralized network that can benefit the entire Web3 community.
Dproxy
Dproxy is the central gateway proxy for DRPC, responsible for receiving user requests and selecting the best data provider to fulfill those requests. To do this, dproxy considers various metrics such as recent performance, current provider status according to the main dshackle, provider capabilities, and the amount of compute units (CUs) that each provider has served recently.
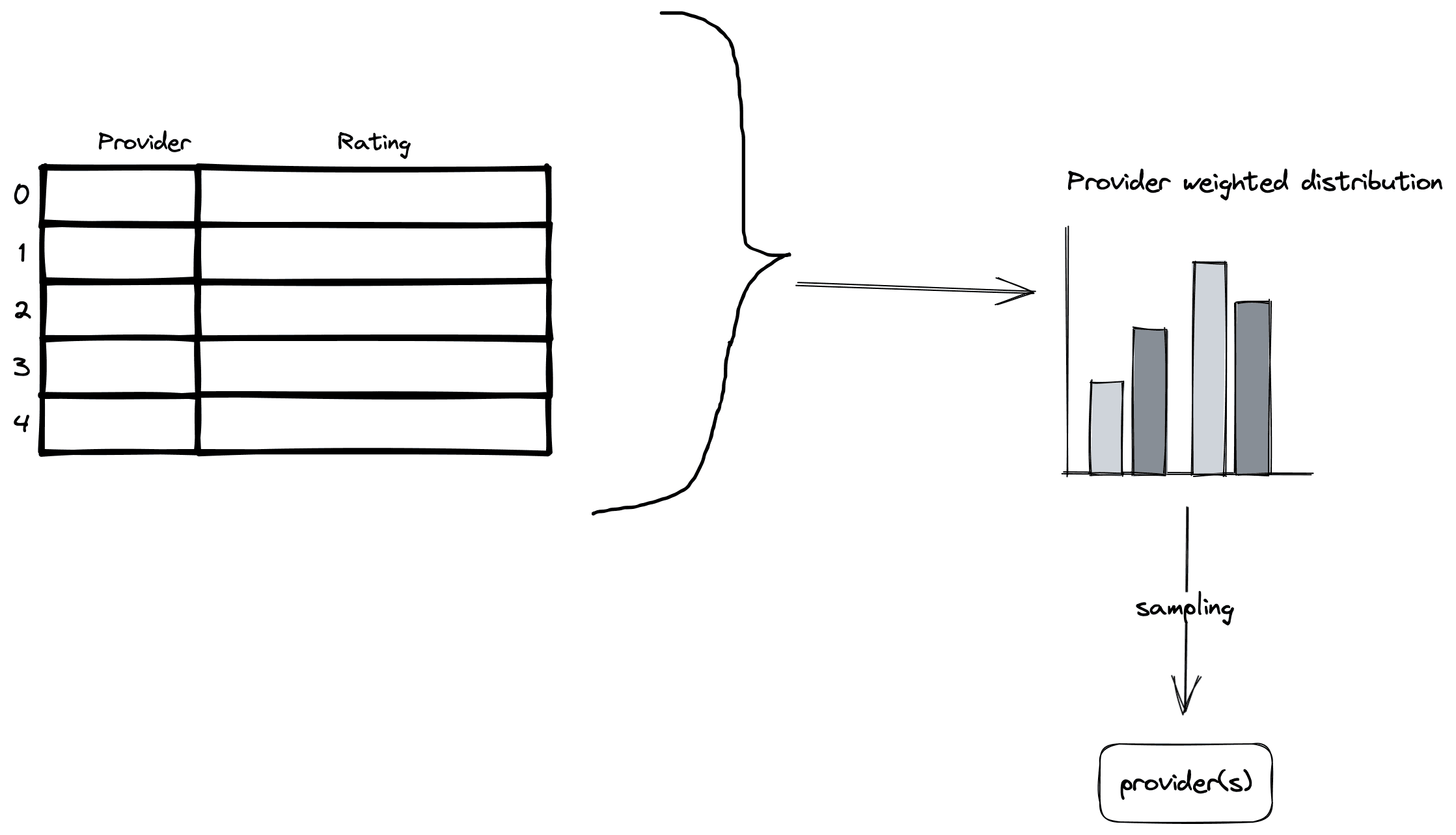
For each provider, Dproxy maintains a rating that is recalculated every second, taking these factors into account. When selecting a provider, Dproxy samples them randomly, with the provider's rating acting as its weight in the distribution. This helps to ensure a smooth load distribution between providers.
In addition to routing requests, dproxy also handles several aspects of the DRPC platform's business logic, including user authorization, deduction of CUs from user balance, and the aggregation of statistics about user requests. Dproxy also provides several additional features, such as verification, specifying custom provider lists for requests, and other functionality to enhance the user experience.